Qt Call Slot Thread
These allow great flexibility and modularity, but how do they work in the context of threads? For example, if an event or slot is triggered in a QObject (which ultimately triggers a function), which thread is calling that function? The answer lies in thread affinity. But let’s back up a bit. Qt threads and Event loops.
When I work with multithreading in Qt at the first time, I feel it really confused with the concepts Signal/Slot. I always have some error about that it can not create threads in QtNetworkManager thread.
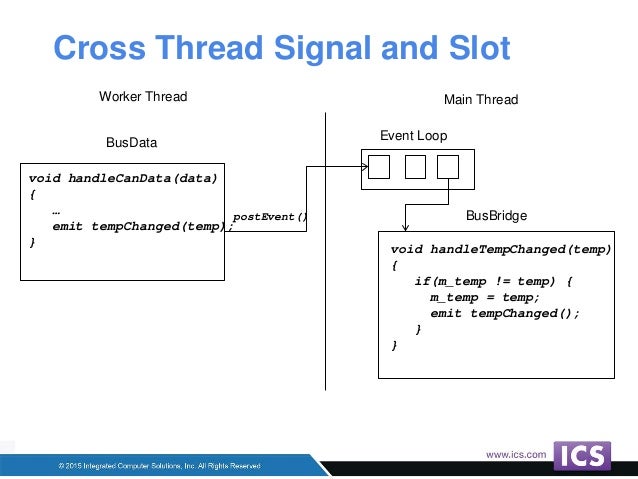
- We call a custom method in the Worker thread instance with the size of the viewer label and the number of stars, obtained from the spin box. Whenever is star is drawn by the worker thread, it will emit a signal that is connected to the addImage slot.
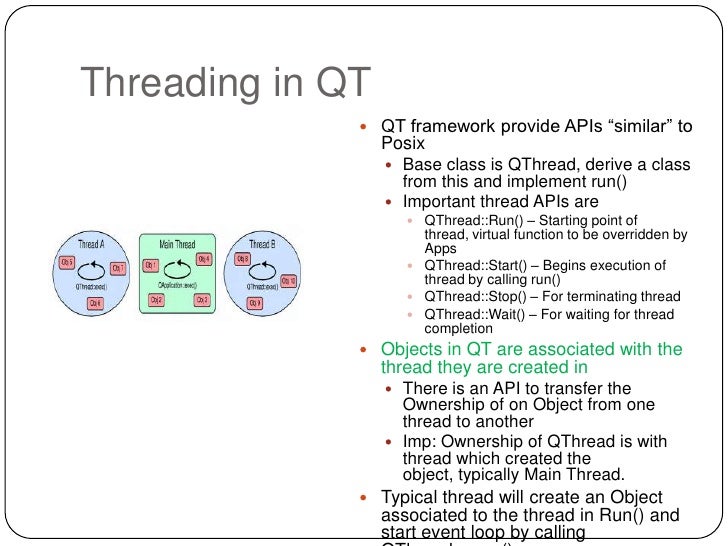
- Detailed Description A QThread object manages one thread of control within the program. QThreads begin executing in run. By default, run starts the event loop by calling exec and runs a Qt event loop inside the thread.
So, in this article, we will discuss about multithreadin in Qt. To go through this article, we will look forward you can easily grasp all of things about multithreading in Qt.
Table of contents
- Introduction to Multithreading in Qt
Introduction to Multithreading in Qt
In Qt, it has own cross-platform implementation of threading. The structure about multithreading in Qt is not as same as multithreading in C++. Qt provides some new features for multithreading such as signal / slot, event loop in each thread, …
As we have already known in Qt, each program has one thread when it is started. This thread is called the main thread or GUI thread in Qt applications. The Qt GUI must run in this thread. All widgets and several related classes, for example QPixmap, do not work in secondary threads. A secondary thread is commonly referred to as a worker thread because it is used to offload processing work from the main thread.
There are basically two use cases for threads:
- Make processing faster by making use of multicore processors.
- Keep the GUI thread or other time critical threads responsive by offloading long lasting processing or blocking calls to other threads.
The QThread is the central class of the Qt threading system to run code in a different thread.
It’s a QObject subclass.
- Not copiable / moveable.
- Has signals to nofify when the thread starts / finishes.
It is meant to manage a thread.
A QThread instance manages one thread of execution within the program.
So, to understand all of knowledge about multithreading, we have to really try hard to completely digest them.
How to use multithread in Qt
Some below steps will be used to create thread in Qt:
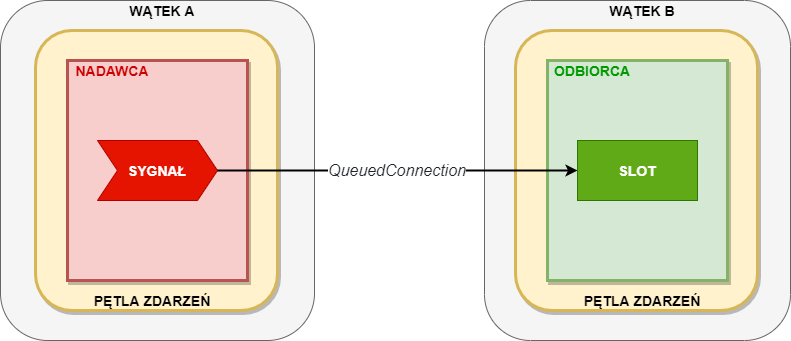
- To create a new thread executing some code, subclass
QThreadand reimplementrun()method. - Then, create an instance of the subclass and call
start(). - Threads have priorities that we can specify as an optional parameter to
start(), or change withsetPriority().
For example:
Some notes in QThread usage:
- The thread will stop running when (some time after) returning from
run(). QThread::isRunning()andQThread::isFinished()provide information about the execution of the thread.- We can also connect to the
QThread::started()andQThread::sleep()functions. Generally, it is a bad idea, being event driven (or polling) is much better. - We can wait for a
QThreadto finish by callingwait()on it. Optionally, passing a maximum number of milliseconds to wait. - Be sure to always destroy all the QObjects living in secondary threads before destroying the corresponding QThread object.
- Do not ever block the GUI thread.
From a non-main thread, we cannot:
- Perform any GUI operation
- Including, but not limited to: using any
QWidget/Qt Quick/QPixmapAPIs. - Using
QImage,QPainteris OK. - Using OpenGL may be OK: check at runtime
QOpenGLContext::supportsThreadedOpenGL().
- Including, but not limited to: using any
- Call
Q(Core Gui)Application::exec().
Ensuring destruction to QObjects:
- Create them on QThread::run() stack.
- Connect their QObject::deleteLater() slot to the QThread::finished() signal.
- Move them out of the thread.
For example:
There are two basic strategies of running code in a separate thread with QThread:
Without an event loop
- Subclass QThread and override QThread::run()
Create an instance and start the new thread via QThread::start().
For example:
With an event loop
- An event loop is necessary when dealing with timers, networking, queued connections, and so on.
Qt supports per-thread event loops
Each thread-local event loop delivers events for the QObjects living in that thread.
For example:
We can start a thread-local event loop by calling QThread::exec() from within run():
QThread::quit()or QThread::exit() will quit the event loop.We can also use QEventLoop or manual calls to QCoreApplication::processEvents().
When to use alternatives to Threads

##
Passing argument to a SLOT
First way: use
QSignalMapperclass.It’s worth noting that in Qt5, C++11,
QSignalMapperis deprecated. From the link: “This class is obsolete. It is provided to keep old source code working. We strongly advise against using it in new code.”Second way: With Qt5 and a C++11 compiler, the idiomatic way to do such things is to give a functor to
connect:The third argument to
connectis nominally optional. It is used to set up the thread context in which the functor will execute. It is always necessary when the functor uses aQObjectinstance. If the functor uses multipleQObjectinstances, they should have some common parent that manages their lifetime and the functor should refer to that parent, or it should be ensured that the objects will outlive the functor.On Windows, this works in MSVC2012 & newer.
Note: If we replace
&QAction::triggeredbySIGNAL(triggered(bool)), and something looks like the below:The compiler will send an error, and the error message will tell us why: there’s no QObject::connect overload that takes a const char * as the 2nd argument and a functor as the third or fourth argument. The Qt4-style connect syntax doesn’t mix with the new syntax. If you wish to use the old syntax, you forfeit the ease of connecting to functors (even though it could be approximated if you had a C++11 compiler but used Qt4).
Third way: use
QObject::sender()in the slot.
How to call Slot in a thread from different thread
Assuming that we have first thread - OurThread class, second thread - AdditionalThread, and slot in OurObject class, then, OurObject will be passed to the AdditionalThread class.
Our problem is that we have to emit a signal from OurThread, and slot in OurObject will be called.
Source code:
In
OurThreadclassIn
AdditionalThreadclassIn OurObject class
In
mainfunction
Wrapping up
- Do not subclass QThread. That’s the starting point for many programmers’ headaches. A QThread is a thread manager, which controls one thread. A QThread is not a thread. Transfer information from thread to thread via signals and slots, using an event-driven approach.
Thanks for your reading.
Qt Call Slot Thread Reducer
Refer: